Vasectomy Failure: Mechanisms, Risk Factors, and Long-Term Outcomes
A vasectomy is widely recognized as one of the most reliable methods of permanent male contraception. Each year, hundreds of thousands of men around the world choose this procedure due to its high efficacy, minimal invasiveness, and low risk of complications. However, like any medical procedure, vasectomy is not without the possibility of failure. Though rare, vasectomy failure can occur, leading to unintended pregnancies and emotional or legal consequences for the individuals involved.
This article explores the mechanisms, risk factors, and long-term outcomes associated with vasectomy failure. Whether you’re a patient considering the procedure or a medical professional providing consultations, understanding these aspects can help in making informed decisions and managing expectations effectively.
Understanding Vasectomy and Its Expected Efficacy
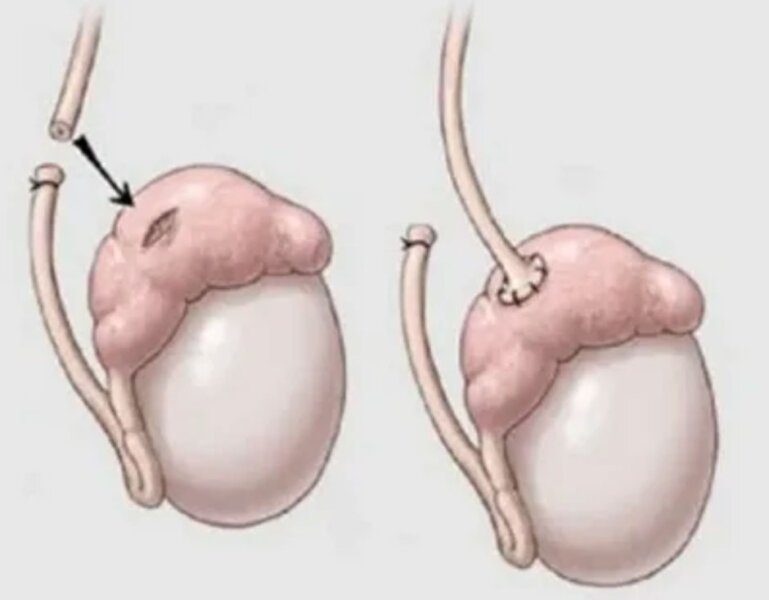
A vasectomy involves cutting, sealing, or blocking the vas deferens—the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles to the urethra. Once the vas deferens are disrupted, sperm can no longer mix with semen, effectively preventing fertilization.
When performed correctly and followed by proper post-operative testing, vasectomy is more than 99% effective. However, vasectomy failure—though it occurs in only about 1 in 2,000 cases—can still happen.
There are two primary types of vasectomy failure:
- Early Failure: Occurs soon after the procedure, usually due to the presence of residual sperm.
- Late Failure: Happens months or even years after a successful vasectomy due to recanalization or incorrect healing.
Mechanisms Behind Vasectomy Failure
Despite being designed as a permanent procedure, vasectomy can fail due to several biological and technical reasons. These mechanisms can be broadly categorized into technical errors, biological healing processes, and patient non-compliance.
1.Recanalization
Recanalization is the most cited biological cause of vasectomy failure. It involves the spontaneous regrowth or reconnection of the severed ends of the vas deferens. This process may allow sperm to once again enter the semen and potentially lead to pregnancy. Recanalization can occur early (within a few months) or late (years later) and is difficult to predict.
2.Technical Errors During Surgery
Improper technique during the vasectomy procedure is another significant reason for failure. If the vas deferens are not fully severed, cauterized, or sealed, sperm may continue to pass through. In rare cases, the wrong tissue is cut or the vas deferens are misidentified, especially in patients with atypical anatomy.
Experienced urologists are less likely to make these errors, which is why choosing a skilled practitioner is essential.
3.Inadequate Post-Vasectomy Semen Analysis (PVSA)
One of the critical steps after a vasectomy is confirming that the procedure was successful through semen analysis. Patients must provide semen samples at intervals recommended by their doctors (typically around 8 to 12 weeks post-op) to ensure that no sperm are present.
Skipping follow-up tests or engaging in unprotected sex too soon after surgery can result in an unintentional pregnancy, mistakenly attributed to vasectomy failure.
Risk Factors for Vasectomy Failure
While the overall risk of vasectomy failure is low, certain factors can increase the likelihood of complications or long-term failure.
1.Surgical Technique Used
There are multiple techniques for performing a vasectomy, including:
- Conventional vasectomy (with a scalpel)
- No-scalpel vasectomy
- Open-ended vs. closed-ended techniques
Some studies suggest that using fascial interposition (placing tissue between the cut ends of the vas deferens) significantly reduces the risk of failure. Not all surgeons utilize this technique, which may lead to higher rates of recanalization.
2.Surgeon Experience
As with any surgical procedure, the experience and precision of the surgeon greatly affect the outcome. A urologist who performs a higher volume of vasectomies is more likely to have refined techniques that reduce the likelihood of technical failure.
3.Patient Anatomy
Individual anatomy differences, such as accessory vas deferens or abnormal tissue structures, can complicate the surgery. These anomalies may lead to incomplete severance or higher chances of natural reconnection.
4.Timing of Postoperative Intercourse
Engaging in sexual activity too soon after a vasectomy can lead to pregnancy if residual sperm are still present. It is recommended that patients wait at least one week before resuming intercourse and continue using alternative contraception until semen tests confirm the absence of sperm.
5.Poor Compliance With Follow-Up
Many cases of vasectomy failure are discovered only after a partner becomes pregnant. This typically occurs when patients fail to attend follow-up appointments or disregard instructions about post-vasectomy testing.
Long-Term Outcomes of Vasectomy Failure
When a vasectomy fails, the implications can be both medical and emotional. Understanding the long-term outcomes can help individuals and couples make appropriate decisions regarding further family planning or potential legal recourse.
1.Unintended Pregnancy
The most immediate and often distressing consequence of vasectomy failure is an unintended pregnancy. In cases where the vasectomy was believed to be successful, this can be particularly shocking.
2.Legal and Ethical Concerns
In some jurisdictions, a failed vasectomy leading to an unintended pregnancy may result in legal claims against the healthcare provider. These cases typically focus on proving negligence, such as improper technique or lack of adequate follow-up care.
3.Repeat Vasectomy or Alternative Procedures
In the event of vasectomy failure, individuals may choose to undergo a second vasectomy or explore alternative methods of contraception, such as female sterilization. The psychological burden of a second surgery can be considerable, especially if the failure occurs years later.
4.Psychological Impact
Couples who experience a vasectomy failure may undergo emotional stress, relationship strain, or anxiety about future pregnancies. Counseling and clear communication with healthcare providers are essential to managing expectations and outcomes.
Preventing Vasectomy Failure
Although it’s impossible to completely eliminate the risk of vasectomy failure, several steps can be taken to minimize it:
- Choose an experienced surgeon
Understand the surgical technique and its success rate - Comply with all post-operative instructions
- Undergo semen analysis until azoospermia (no sperm) is confirmed
- Use alternative contraception until cleared by a doctor
The combination of good surgical practice and diligent patient compliance remains the best way to ensure long-term success after a vasectomy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1.Can a vasectomy fail years after the procedure?
Yes, although rare, late vasectomy failure can occur due to spontaneous reconnection of the vas deferens (recanalization). This can happen even years after the procedure. Regular follow-ups and early pregnancy detection are important in long-term monitoring.
2.What are the signs that a vasectomy has failed?
The most common sign of vasectomy failure is an unplanned pregnancy. Other signs might include the presence of sperm in post-operative semen analysis or, very rarely, pain or swelling in the testicles if recanalization causes blockage or inflammation.
3.How can I reduce the risk of vasectomy failure?
To reduce the risk of failure, choose an experienced surgeon, ensure proper post-operative testing, and avoid sexual activity until cleared by your doctor. It’s also important to confirm that your partner does not become pregnant before sperm clearance is verified.
Conclusion
While a vasectomy remains one of the most effective forms of male sterilization, it’s not foolproof. Vasectomy failure, though uncommon, can occur due to biological healing processes, surgical technique, or patient non-compliance. Understanding these risks, selecting the right provider, and following through with proper aftercare are essential to maximizing the success of the procedure.
Men considering this form of contraception should be fully informed of its effectiveness, as well as the small but real chance of failure. By being proactive and engaged in the process, patients can confidently move forward with their decision, knowing they’ve minimized their risk of vasectomy failure.